Sparus aurata
transcriptomic and genomic database
About the project
The gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) is the main teleost species cultured in the Mediterranean area and a major goal of our research group is to integrate genomic and transcriptomic data to assist fish phenotyping and the development of biomarker panels of prognostic and diagnostic value.
About the gilthead sea bream genome project
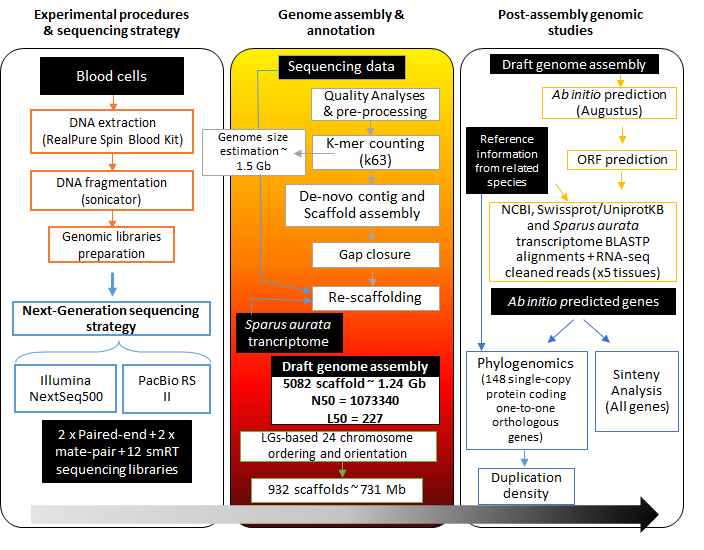
The present genomic database comprises assembled data of 5,039 scaffolds that span 1.24 Gb of the expected 1.59 Gb complete genome size. A total of 932 scaffolds (~732 Mb) were anchored to 24 chromosomes. The assembly was reconstructed by combining short- (Illumina NextSeq 500) and long-read (PacBio RS II) sequencing strategy, and genetic linkage maps. The long and continuous reads allowed the prediction of 78,238 coding regions. Transcriptional analysis across six different tissues (anterior and posterior intestine, skeletal muscle, liver, spleen and gills) rendered the annotation of 55,423 actively transcribed protein-coding genes. Furthermore, 2,991 non-coding RNA genes and 345 Mb of mobile genetic elements were located and placed through the genome sequence.
The construction of the genome database has been funded under Spanish (Intramural CSIC, 1201530E025; MICINN BreamAquaINTECH, RTI2018-094128-B-I00) and European Union (AQUAEXCEL2020, 652831) projects.
About the gilthead sea bream transcriptome project
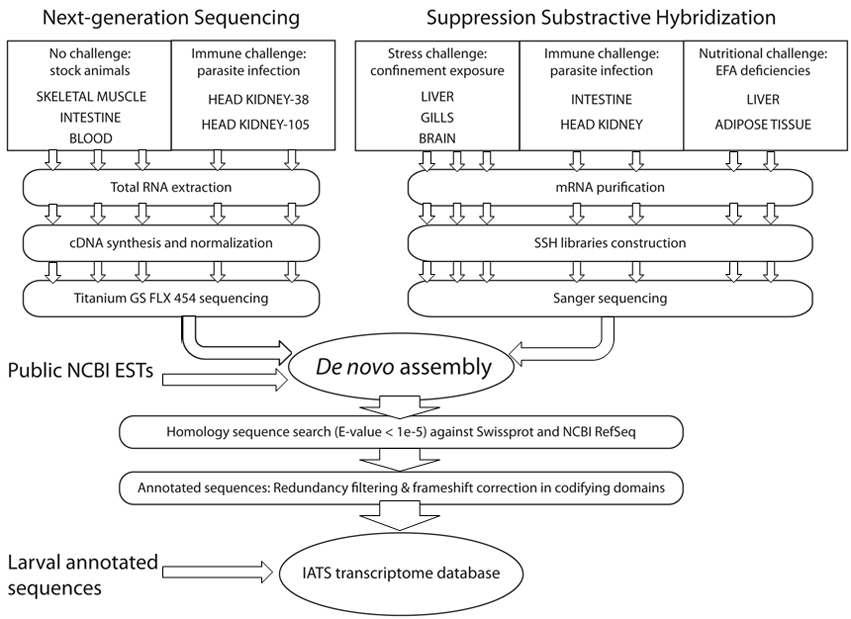
The present transcriptome database collects assembled data derived from public repositories of mRNA, collections of expressed sequence tags (suppressive subtractive hybridization (SSH) libraries of fish challenged with environmental, pathogenic and nutritional stressors) together with new high-quality reads from five cDNA 454 normalized libraries of metabolically and immunologically relevant tissues (skeletal muscle, intestine, head kidney, and blood). It has been recently updated with the addition of annotated sequences from pyrosequencing of 454 libraries of larval origin (Yúfera et al., 2012).
The construction of the transcriptome database has been funded under EU seventh Framework Programme by projects ARRAINA (Advanced Research Initiatives for Nutrition & Aquaculture, FP7/2007-2013; grant agreement nº 288925) and AQUAEXCEL (Aquaculture Infrastructures for Excellence in European Fish Research, FP7/2007-2012; grant agreement nº 262336). Additional funding was obtained by Generalitat Valenciana (research grant PROMETEO 2010/006) and Spanish Government through AQUAGENOMICS (Ingenio-2010 Programme), AQUAFAT (AGL2009-07797) and ENTEROMYXCONTROL (AGL2009-13282-C02-01) projects.






